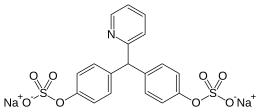
Sodium picosulfate
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Picosulfuric acid |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.097 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H15NNa2O9S2 |
| Molar mass | 499.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
| | |
Sodium picosulfate (INN, also known as sodium picosulphate) is a contact stimulant laxative used as a treatment for constipation or to prepare the large bowel before colonoscopy or surgery.
It is available as a generic medication.[2]
Medical uses
[edit]Sodium picosulfate used in combination with magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid is indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy.[1]
Effects
[edit]Orally administered sodium picosulfate is generally used for thorough evacuation of the bowel, usually for patients who are preparing to undergo a colonoscopy. It takes 12–24 hours to work, since it works in the colon.[3]
Abdominal cramps and diarrhea are normal effects of picosulfate and should be expected.
The use of sodium picosulfate has also been associated with certain electrolyte disturbances, such as hyponatremia and hypokalemia.[4] Patients are often required to drink large amounts of clear fluids, to compensate for dehydration and to reestablish normal electrolyte balance.
Mechanism of action
[edit]Sodium picosulfate is a prodrug.[5] It has no significant direct physiological effect on the intestine; however, it is metabolised by gut bacteria into the active compound 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl-(2-pyridyl)methane (DPM, BHPM).[5][6] This compound is a stimulant laxative and increases peristalsis in the gut.[5][7]
Sodium picosulfate is typically prescribed in a combined formulation with magnesium citrate, an osmotic laxative. This combination is a highly effective laxative, often prescribed to patients for bowel cleansing prior to colonoscopies.[5][8]
Society and culture
[edit]Brand names
[edit]It is sold under the brand names Sodipic Picofast, Laxoberal, Laxoberon,[9] Purg-Odan, Picolax, Guttalax, Namilax, Pico-Salax,[10] PicoPrep,[11] and Prepopik,[3] among others.
Clenpiq is a combination of sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and citric acid.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Clenpiq- sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid liquid". DailyMed. 5 September 2023. Retrieved 30 December 2023.
- ^ "2022 First Generic Drug Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 3 March 2023. Archived from the original on 30 June 2023. Retrieved 30 June 2023.
- ^ a b "FDA News Release – FDA approves new colon-cleansing drug for colonoscopy prep". Food and Drug Administration. 17 July 2012. Retrieved 1 December 2016.
- ^ ADRAC (February 2002). "Electrolyte disturbances with sodium picosulfate bowel cleansing products". Aust Adv Drug React Bull. 21 (1). Free full text Archived 22 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine from the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration
- ^ a b c d Adamcewicz M, Bearelly D, Porat G, Friedenberg FK (January 2011). "Mechanism of action and toxicities of purgatives used for colonoscopy preparation". Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology. 7 (1): 89–101. doi:10.1517/17425255.2011.542411. PMC 3030244. PMID 21162694.
- ^ Forth W, Nell G, Rummel W, Andres H (1 March 1972). "The hydragogue and laxative effect of the sulfuric acid ester and the free diphenol of 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl-(pyridyl-2)-methane". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 274 (1): 46–53. doi:10.1007/BF00501005. PMID 4262724. S2CID 13177533.
- ^ Jauch R, Hankwitz R, Beschke K, Pelzer H (November 1975). "Bis-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane: The common laxative principle of Bisacodyl and sodium picosulfate". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 25 (11): 1796–1800. PMID 1243088.
- ^ Regev A, Fraser G, Delpre G, Leiser A, Neeman A, Maoz E, et al. (September 1998). "Comparison of two bowel preparations for colonoscopy: sodium picosulphate with magnesium citrate versus sulphate-free polyethylene glycol lavage solution". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 93 (9): 1478–82. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00467.x. PMID 9732929. S2CID 7579449.
- ^ Website of Merck Pakistan
- ^ PICO SALAX Product Information Archived 22 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Tjandra JJ, Chan M, Tagkalidis PP (May 2006). "Oral sodium phosphate (Fleet) is a superior colonoscopy preparation to Picopre (sodium picosulfate-based preparation)". Diseases of the Colon and Rectum. 49 (5): 616–20. doi:10.1007/s10350-005-0323-2. PMID 16525746. S2CID 36729352.
